Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), available at $44.99, has an average rating of 4.25, with 20 lectures, 4 quizzes, based on 96 reviews, and has 318 subscribers.
You will learn about Introduction and Historical Background of Next Generation Sequencing What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)? Key Principle behind NGS Difference between Sanger sequencing and NGS Sample preparation (Pre-processing) for NGS Library Preparation for NGS PCR Amplification for NGS including Emulsion PCR and Bridge PCR 454 Pyrosequencing approcah Sequencing by ligation (SOLiD) approach Ion torrent semiconductor sequencing approach Reversible terminator sequencing (illumina) approach Sequencing read types including single end and paired end reads Data Analysis (Post-processing) for NGS key considerations when selecting sequencing strategy Strengths and Limitations of Next Generation Sequencing Applications of Next Generation Sequencing Third and Fourth Generation Technologies This course is ideal for individuals who are Students who want to go for bioltechnologist, lab technologist and molecular biologists job. or The course is designed for researchers of molecular biology, biotechnology, and related disciplines. or Students who wants to persude their career in sequencing analysis, forensic science, research, molecular biology, clinincal analysis and genetics. It is particularly useful for Students who want to go for bioltechnologist, lab technologist and molecular biologists job. or The course is designed for researchers of molecular biology, biotechnology, and related disciplines. or Students who wants to persude their career in sequencing analysis, forensic science, research, molecular biology, clinincal analysis and genetics.
Enroll now: Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Summary
Title: Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Price: $44.99
Average Rating: 4.25
Number of Lectures: 20
Number of Quizzes: 4
Number of Published Lectures: 20
Number of Published Quizzes: 4
Number of Curriculum Items: 24
Number of Published Curriculum Objects: 24
Original Price: $22.99
Quality Status: approved
Status: Live
What You Will Learn
- Introduction and Historical Background of Next Generation Sequencing
- What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
- Key Principle behind NGS
- Difference between Sanger sequencing and NGS
- Sample preparation (Pre-processing) for NGS
- Library Preparation for NGS
- PCR Amplification for NGS including Emulsion PCR and Bridge PCR
- 454 Pyrosequencing approcah
- Sequencing by ligation (SOLiD) approach
- Ion torrent semiconductor sequencing approach
- Reversible terminator sequencing (illumina) approach
- Sequencing read types including single end and paired end reads
- Data Analysis (Post-processing) for NGS
- key considerations when selecting sequencing strategy
- Strengths and Limitations of Next Generation Sequencing
- Applications of Next Generation Sequencing
- Third and Fourth Generation Technologies
Who Should Attend
- Students who want to go for bioltechnologist, lab technologist and molecular biologists job.
- The course is designed for researchers of molecular biology, biotechnology, and related disciplines.
- Students who wants to persude their career in sequencing analysis, forensic science, research, molecular biology, clinincal analysis and genetics.
Target Audiences
- Students who want to go for bioltechnologist, lab technologist and molecular biologists job.
- The course is designed for researchers of molecular biology, biotechnology, and related disciplines.
- Students who wants to persude their career in sequencing analysis, forensic science, research, molecular biology, clinincal analysis and genetics.
Over the last 56 years, researchers have been developing methods and technologies to assist in the determination of nucleic acid sequences in biological samples. The ability to sequence DNA and RNA accurately has had a great impact in numerous research fields. The sequencing of the human genome was completed in 2003, after 13 years of international collaboration and investment of USD 3 billion. The Human Genome Project used Sanger sequencing, the principal method of DNA sequencing since its invention in the 1970s. Today, the demand for sequencing is growing exponentially, with large amounts of genomic DNA needing to be analyzed quickly, cheaply, and accurately. Thanks to new sequencing technologies known collectively as Next Generation Sequencing.
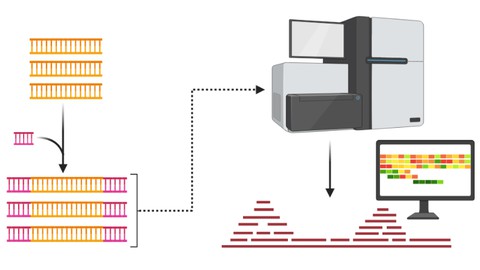
Next generation sequencing (NGS), also known as high throughput sequencing or second generation sequencing or short read sequencing, is a massively parallel sequencing technology that offers ultra-high throughput, scalability, and speed. The technology is used to determine the order of nucleotidesin entire genomes or targeted regions of DNA or RNA.
The main difference between Sanger sequencing and NGS stems from sequencing volume, with NGS allowing the processing of millions of reactions in parallel, resulting in high-throughput, higher sensitivity, speed and reduced cost. A plethora of genome sequencing projects that took many years with Sanger sequencing methods could now be completed within hours using NGS.
There are several main steps that must be tailored to the target (RNA or DNA) and sequencing system selected. The main steps of NGS includes sample preparation (pre-processing), library preparation, PCR amplification, sequencingand data analysis (Post-processing).
Library preparationincludes DNA fragmentation either enzymatically or by sonication, end repairing and adaptor ligation.
Library amplification is required so that the received signal from the sequencer is strong enough to be detected accurately. The two most common PCR amplification methods are emulsion PCRand bridge PCR.
Several competing methods of NGS have been developed by different companies including 454 Pyrosequencing, sequencing by ligation (SOLiD), ion torrent semiconductor sequencing and reversible terminator sequencing (illumina).
NGS can generate two types of reads i.e, single end reads and paired end reads, depending on method of choice.
NGS has enabled researchers to collect vast quantities of genomic sequencing data. This technology has a plethora of applications, such as: outbreak Management,diagnosing and understanding complex diseases, whole-genome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, cancer treatments, detection of viruses, surveillance of antimicrobial resistance and many more.
Now, third (3G) and fourth (4G) generation technologies have been evolved that work on different underlying principles.
This course is a valuable resource for students and researchers related to molecular biology, forensic science, medical laboratory technology, biotechnology, and genetics.
Start your learning journey now and explore the hidden truth about sequencing technology!
Course Curriculum
Chapter 1: Overview
Lecture 1: Overview
Chapter 2: Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Lecture 1: Introduction and Historical Background
Lecture 2: What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
Lecture 3: Key Principle behind Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Lecture 4: Difference between Sanger sequencing and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Chapter 3: Main Steps of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Lecture 1: Sample Preparation (Pre-processing)
Lecture 2: Library Preparation
Lecture 3: PCR Amplification
Lecture 4: Sequencing: 1. Pyrosequencing
Lecture 5: Sequencing: 2. Sequencing by ligation (SOLiD)
Lecture 6: Sequencing: 3. Ion torrent semiconductor sequencing
Lecture 7: Sequencing: 4. Reversible terminator sequencing (Illumina)
Lecture 8: Sequencing Read Types
Lecture 9: Data Analysis (Post-processing)
Lecture 10: key Considerations When Selecting Sequencing Strategy
Lecture 11: Resource
Chapter 4: Strengths and Limitations of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Lecture 1: Strengths of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Lecture 2: Limitations of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Chapter 5: Applications of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Lecture 1: Applications of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Chapter 6: Third and Fourth Generation Technologies
Lecture 1: Third and Fourth Generation Technologies
Instructors
-
Anum Ahmad, PhD
Educator
Rating Distribution
- 1 stars: 4 votes
- 2 stars: 4 votes
- 3 stars: 17 votes
- 4 stars: 36 votes
- 5 stars: 35 votes
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do I have access to the course materials?
You can view and review the lecture materials indefinitely, like an on-demand channel.
Can I take my courses with me wherever I go?
Definitely! If you have an internet connection, courses on Udemy are available on any device at any time. If you don’t have an internet connection, some instructors also let their students download course lectures. That’s up to the instructor though, so make sure you get on their good side!
You may also like
- Best Emotional Intelligence Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Time Management Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Remote Work Strategies Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Freelancing Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best E-commerce Strategies Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Personal Branding Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Stock Market Trading Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Real Estate Investing Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Financial Technology Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Agile Methodologies Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Project Management Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Leadership Skills Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Public Speaking Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Affiliate Marketing Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Email Marketing Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Social Media Management Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best SEO Optimization Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Content Creation Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Game Development Courses to Learn in March 2025
- Best Software Testing Courses to Learn in March 2025






















